ATP/ADP ratio, the missed connection between mitochondria and the Warburg effect


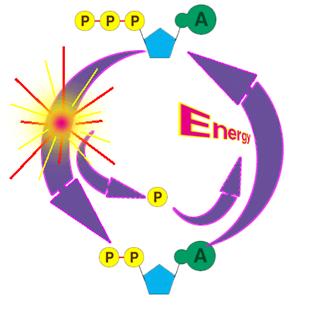
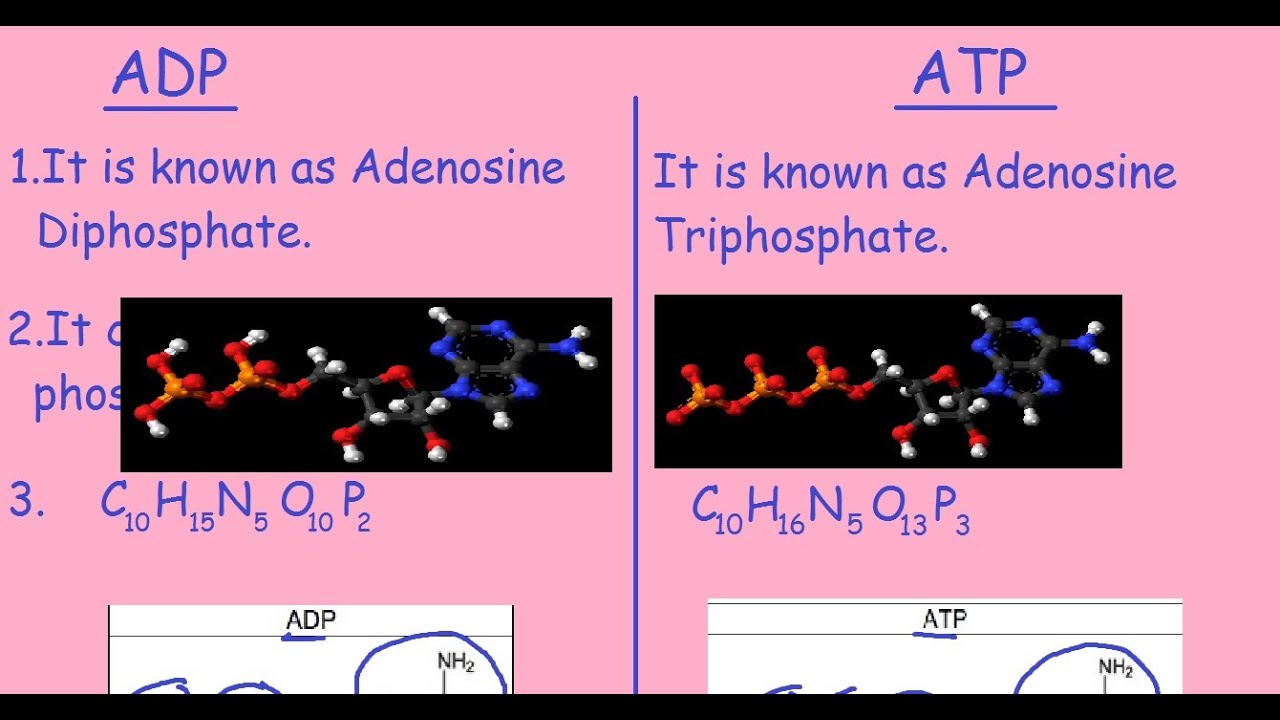
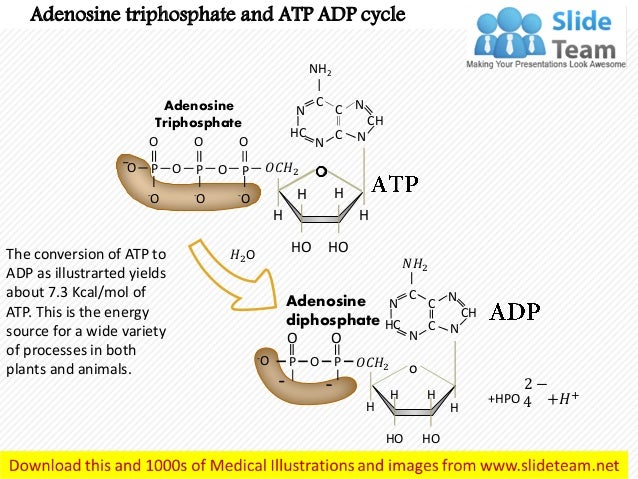
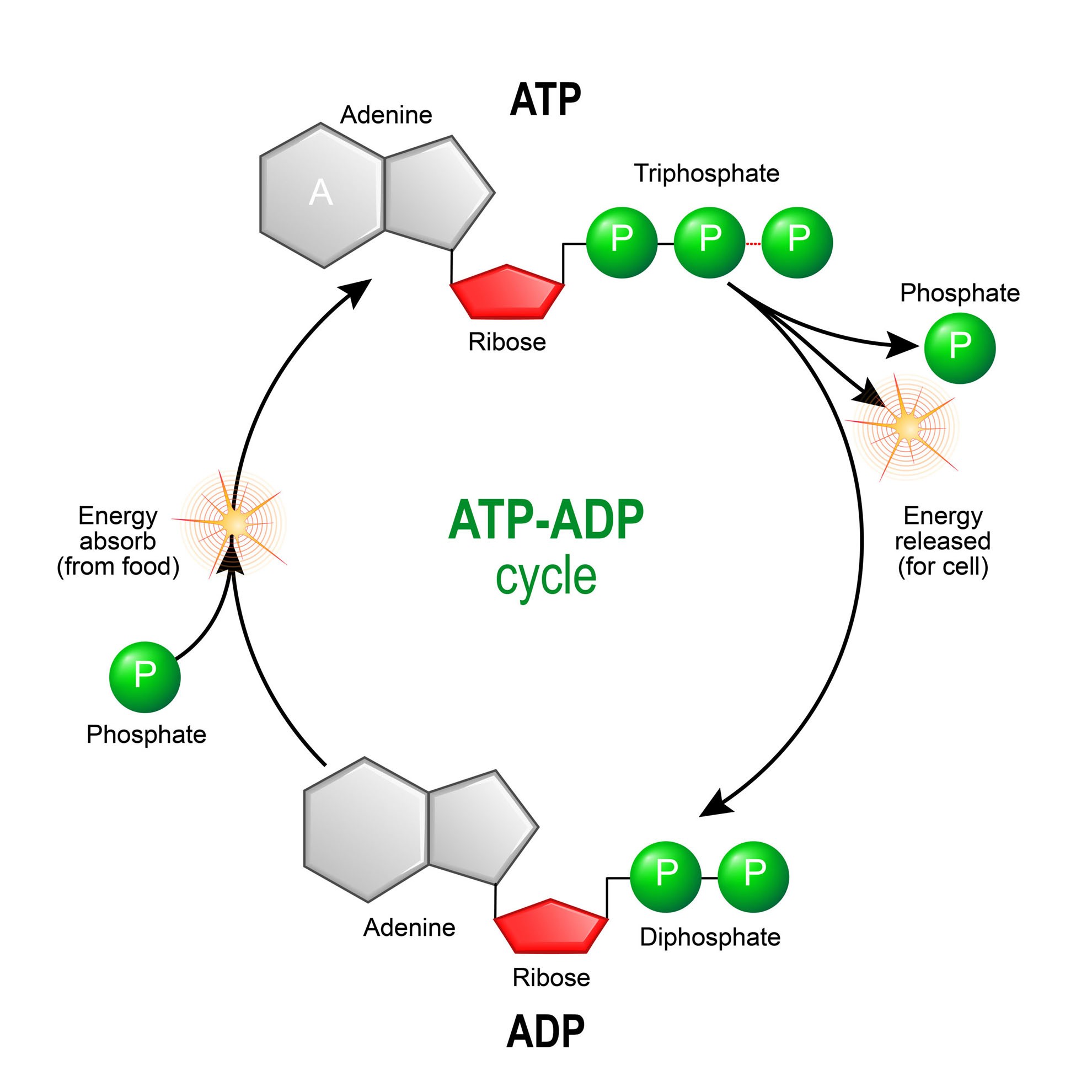
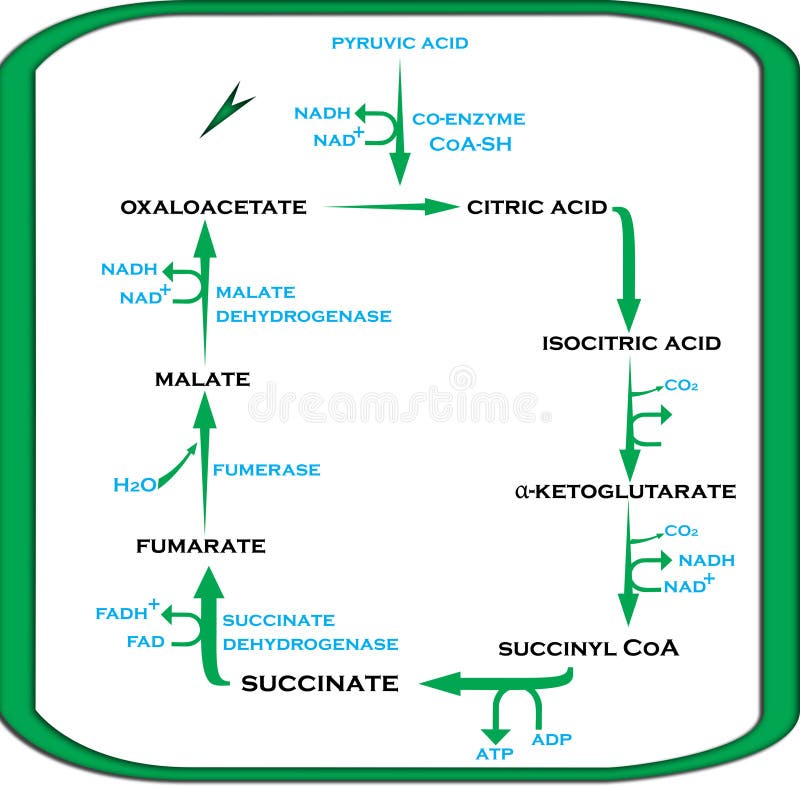
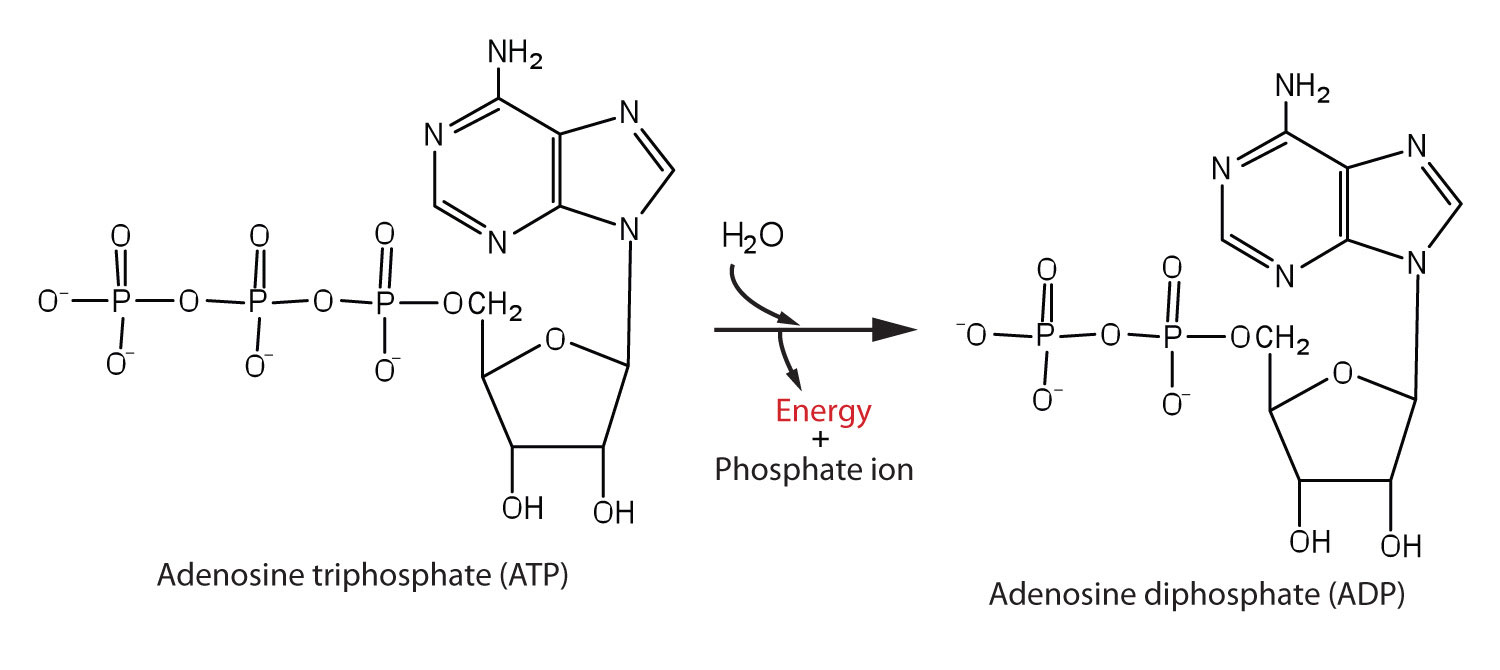
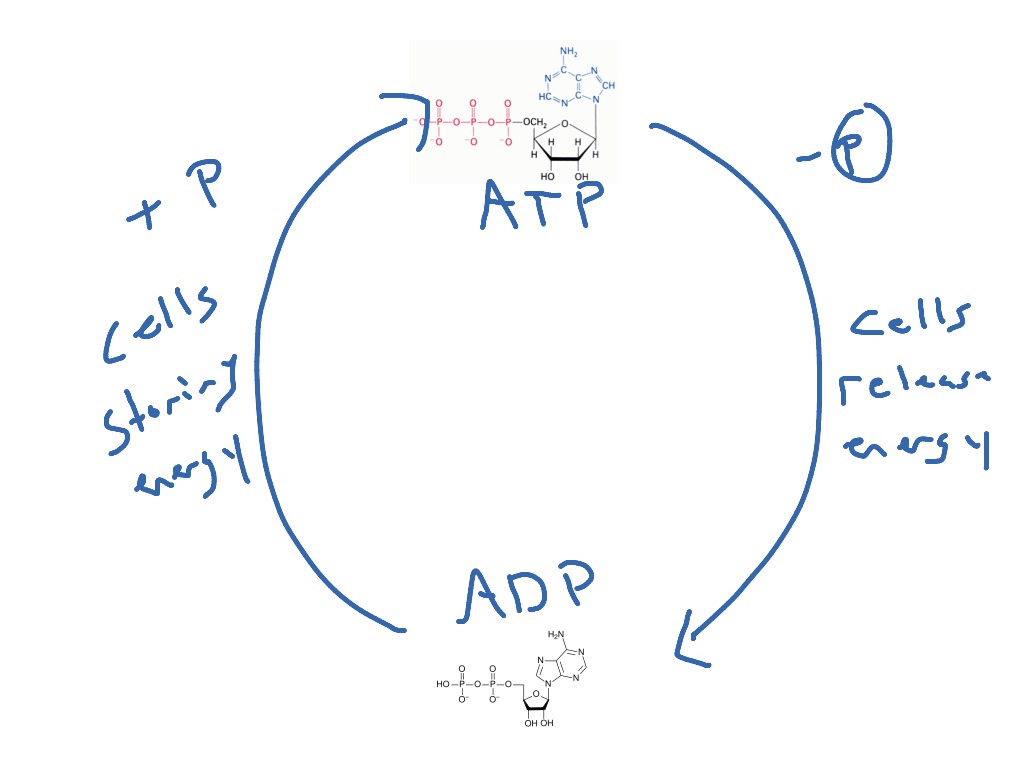
In contrast, the second family, which includes BA and isobongkrekic acid isoBA , binds the translocase from the matrix, locking it in a matrix side open conformation. If exercise continues longer, then the glycogen-lactic acid system kicks in. Kunji ER, Crichton PG March 2010. "A second magnesium ion is critical for ATP binding in the kinase domain of the oncoprotein v-Fps". Free ADP is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix, while ATP produced from is transported from the to the , thus providing the cells with its main energy currency. Protons return into the matrix through the F 1-F 0-ATP synthase Complex V driving synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi. Industry You face specific challenges that require solutions based on experience. Ribose sugar: It is the pentose sugar found intermediary between the adenine and phosphoryl group. Ribose pentose sugar• Binding of ATP from the matrix induces eversion and results in the release of ATP into the intermembrane space, subsequently diffusing to the cytoplasm, and concomitantly brings the translocase back to its original conformation. You starve the fire of oxygen, and the flame flickers out. In step 3, phosphofructokinase PFK take a phosphate from ATP and add the phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate to create fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Main article: Ketone bodies can be used as fuels, yielding 22 ATP and 2 molecules per acetoacetate molecule when oxidized in the mitochondria. Both are constantly interconverted and regenerated inside a body. Cells detect ATP using the proteins P2X and P2Y. ATP is required for the phosphorylation of glucose, creating a high-energy but unstable intermediate. Similarly, a cell must need a particular source of energy to perform specific tasks. It is considered as the energy currency of life. When ATP is hydrolyzed, it transfers its gamma phosphate to the pump protein in a process called phosphorylation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy-releasing exergonic reactions, which require a small input of activation energy. "Chelation of divalent cations by ATP, studied by titration calorimetry". ATP recycling [ ] The total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0. Glycolysis• ATP is also useful in many cell processes such as photosynthesis, anaerobic respiration, and active transport across cell membranes, etc. sequenced a cDNA clone of the human transporter in 1989. Molecular Structure Adenosine triphosphate ATP is comprised of the molecule adenosine bound to three phosphate groups. Therefore, due to , the reaction spontaneously occurs because it wants to be at a higher entropy level. hydrolysis: A chemical process of decomposition involving the splitting of a bond by the addition of water. Main articles: and In the , pyruvate is oxidized by the to the group, which is fully oxidized to by the also known as the Krebs cycle. OpenStax College, Biology. External links [ ]• It took a lot of energy to organize those blocks into that complex structure, and breaking the blocks apart releases that energy and frees the blocks so that they can be built back up into new things. Key Terms• If a metabolic reaction is aerobic, it requires oxygen. Remaining glycogen supplies in the muscles• The content on this website is for information only. When the cell has extra energy gained from breaking down food that has been consumed or, in the case of plants, made via photosynthesis , it stores that energy by reattaching a free phosphate molecule to ADP, turning it back into ATP. In a neutral solution, ATP has negatively charged groups that allow it to chelate metals. ADP in the intermembrane space, coming from the cytoplasm, binds the translocase and induces its eversion, resulting in the release of ADP into the matrix. Public Domain; via Wikipedia. After this happens, the newly bound ATP is converted to ADP and inorganic phosphate, P i. Once the tropomyosin is removed, a cross-bridge can form between actin and myosin, triggering contraction. — the ion that gives its name to the cycle — is a feedback inhibitor of and also inhibits PFK, providing a direct link between the regulation of the citric acid cycle and glycolysis. ATP comes from three different biochemical systems in the muscle, in this order:• Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. When the power of the battery reduces, it indicates the loss of energy. Worldwide Locations We provide payroll, global HCM and outsourcing services in more than 140 countries. After the power stroke, ADP is released; however, the cross-bridge formed is still in place, and actin and myosin are bound together. Regulatory Proteins When a muscle is in a resting state, actin and myosin are separated. Steps 1 and 3 of glycolysis are referred to as "Priming Steps". It is the end-product when ATP loses one of its phosphate groups. Living cells maintain the ratio of ATP to ADP at a point ten orders of magnitude from equilibrium, with ATP concentrations fivefold higher than the concentration of ADP. ATP can be considered as the potential energy, which is basically the stored energy that can be used by a cell to do particular tasks. Phosphate: The phosphoryl group is joined to the 5 th carbon atom of the ribose sugar. ATP analogues [ ] Biochemistry laboratories often use studies to explore ATP-dependent molecular processes. Ribose sugar: It is the pentose sugar, located intermediary between the adenine and phosphoryl group. The phosphagen system can supply the energy needs of working muscle at a high rate, but only for 8 to 10 seconds. Helps in catabolism reactions, in the activation of platelets etc. The ANT and the are not necessarily in directional synchrony. Unless otherwise noted, LibreTexts content is licensed by. at the US National Library of Medicine MeSH• Ruprecht JJ, Hellawell AM, Harding M, Crichton PG, McCoy AJ, Kunji ER January 2014. Who We Serve See how we help organizations like yours with a wider range of payroll and HR options than any other provider. 5 of enthalpy, with a change in of 3. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional prior to beginning any diet or exercise program or taking any dietary supplement. adPEO shows patterns but is characterized by large-scale mtDNA deletions. Main article: In glycolysis, glucose and glycerol are metabolized to. It is also a to and , and is used as a. When the chemical bonds within ATP are broken, energy is released and can be harnessed for cellular work. Where is ATP synthase located? The molecular formula of ATP is C 10H 16N 5O 13P 3. ATP vs ADP ATP is a nucleotide which contains high energy in two phosphoanhydride known as the energy currency of life. The structure of Adenosine di-phosphate includes three distinct groups:• HepG2 cells were loaded with TMRM, as described in Fig. When the bond connecting the phosphate is broken, energy is released. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. History [ ] ATP was discovered in 1929 by and Jendrassik and, independently, by Cyrus Fiske and of , both teams competing against each other to find an assay for phosphorus. Talent From recruitment to retirement, getting the very best out of your people. Molecular and Cellular Biology. Key Takeaways Key Points• Demos Discover how easy and intuitive it is to use our solutions. Six arginines and one lysine are essential". Functions of ATP promotes active transport, the building of molecules, cellular functions like muscle movement,while ADP helps in catabolic reactions, activation of platelets etc. What happens if you put a glass over a candle? Regulation [ ] In glycolysis, is directly inhibited by its product, glucose-6-phosphate, and is inhibited by ATP itself. About ADP ADP helps organizations of all types and sizes unlock their potential. This creates a difference in hydrogen cation concentration. mtDNA contains few , or non-coding regions of DNA, which increases the likelihood of deleterious. The functional coupling between mitochondrial creatine phosphokinase and ATP ADP translocase: kinetic evidence". ADP is an organic compound which mediates the energy flow in the cells. Glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules. It has a mass of approximately 30 kDa, consisting of 297 residues. , a sugar that is delivered via the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and this is the molecule that is used to create ATP. Aerobic respiration would use carbohydrates first, then fats and finally proteins, if necessary. CC licensed content, Specific attribution• "Mitochondrial carriers function as monomers". The terminal phosphate group of ATP removes and produces ADP. Ruprecht JJ, Hellawell AM, Harding M, Crichton PG, McCoy AJ, Kunji ER January 2014. Myosin has another binding site for ATP at which enzymatic activity hydrolyzes ATP to ADP, releasing an inorganic phosphate molecule and energy. energy coupling: Energy coupling occurs when the energy produced by one reaction or system is used to drive another reaction or system. Karch J, Bround MJ, Khalil H, et al. Credit: Respiration and the Creation of ATP ATP is created via respiration in both animals and plants. It is known as the energy currency of life in all organisms including bacteria to humans and its value is only second to of the cell. This can only happen in the presence of calcium, which is kept at extremely low concentrations in the sarcoplasm. Most of the ATP synthesized in the mitochondria will be used for cellular processes in the cytosol; thus it must be exported from its site of synthesis in the mitochondrial matrix. Saks VA, Lipina NV, Smirnov VN, Chazov EI March 1976. A number of other small molecules can compensate for the ATP-induced shift in equilibrium conformation and reactivate PFK, including , ions, inorganic phosphate, and fructose-1,6- and -2,6-biphosphate. Every "turn" of the citric acid cycle produces two molecules of carbon dioxide, one equivalent of ATP GTP through catalyzed by , as succinyl- CoA is converted to Succinate, three equivalents of , and one equivalent of. The , which is the level of disorder, of ADP is greater than that of ATP. Main article: In the presence of air and various cofactors and enzymes, fatty acids are converted to. ATP serves as a neurotransmitter in many parts of the nervous system, modulates ciliary beating, affects vascular oxygen supply etc. The human genome encodes 48 ABC transporters, that are used for exporting drugs, lipids, and other compounds. DOI: Free PMC article• symbols ANT2 Other data Search for Structures Domains solute carrier family 25 mitochondrial carrier; adenine nucleotide translocator , member 6 Identifiers Symbol Alt. The oxygen molecules of the ADP are sharing electrons. Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition by deletion of the ANT family and CypD. Lactic acid builds up in the muscle tissue and causes the fatigue and soreness you feel in your exercising muscles. This makes ATP a relatively unstable molecule because it will want to give away its phosphate groups, when given the chance, in order to become a more stable molecule. In the absence of oxygen, the citric acid cycle ceases. Click any text name of pathway or metabolites to link to the corresponding article. and Mitochondria Research Society. Kunji ER, Harding M September 2003. For example, it takes only a few seconds for half of the ATP molecules in a cell to be converted into ADP to be used in driving endergonic non-spontaneous reactions and then converted back into ATP using exergonic spontaneous reactions. The protein is in the open conformation towards this side. Energy Coupling in Sodium-Potassium Pumps Energy Coupling: Sodium-potassium pumps use the energy derived from exergonic ATP hydrolysis to pump sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane. Pfaff E, Klingenberg M, Heldt HW June 1965. propose a "multi-pore model" in which ANT is at least one of the molecular components of the pore. This movement is called the power stroke, as it is the step at which force is produced. Annual Review of Biochemistry. The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the myosin head. Brandolin G, Dupont Y, Vignais PV April 1985. Introduction ATP is an unstable molecule which hydrolyzes to ADP and inorganic phosphate when it is in equilibrium with water. Events Attend webinars or find out where and when we can connect at in-person events. The cycles of synthesis and degradation of ATP; 2 and 1 represent input and output of energy, respectively. Adapted from Maldonado, et al. The energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP is used to perform cellular work, usually by coupling the exergonic reaction of ATP hydrolysis with endergonic reactions. The process of respiration occurs in 3 steps when oxygen is present :• If actin binding sites are covered and unavailable, the myosin will remain in the high energy configuration with ATP hydrolyzed, but still attached. Out of those, the last step produces ATP. "Photosynthesis of ATP-electrons, proton pumps, rotors, and poise". This action requires energy, which is provided by ATP. The entire reaction that turns ATP into energy is a bit complicated, but here is a good summary:• It serves as the energy source, necessary for all the life forms, which fuels different cells to promote specific functions. Your body does exactly that when you eat your food. While ATP is constantly being used up by the body in its biological processes, the energy supply can be bolstered by new sources of glucose being made available via eating food which is then broken down by the digestive system to smaller particles that can be utilized by the body. ATP and ADP are composed of three components known as adenine base, and phosphate groups. It is also handy because the rapidly contracting muscle squeezes off its own blood vessels, depriving itself of oxygen-rich blood. True or false: ATP may be used to regulate certain. ADP is also important during the activation of platelets. Here's a brief that summarizes this concept. This form of signal transduction is particularly important in brain function, although it is involved in the regulation of a multitude of other cellular processes. In addition, the key differences and similarities of the two have been also explained. Adrian GS, McCammon MT, Montgomery DL, Douglas MG February 1986. The process of ATP formation from ADP is an endergonic reaction consumes energy , whereas the process of ADP formation from ATP is an exergonic reaction dissipates energy. Figure 1: ATP Structure ATP molecules provide energy for all biochemical reactions in the body by ATP converting into ADP. In the context of biochemical reactions, the P-O-P bonds are frequently referred to as. ATP is useful in many cell processes such as , , , , active transport across cell membranes as in the , and synthesis of macromolecules such as. In its many reactions related to metabolism, the adenine and sugar groups remain unchanged, but the triphosphate is converted to di- and monophosphate, giving respectively the derivatives and. Ketone bodies are transported from the to other tissues, where and can be reconverted to to produce reducing equivalents NADH and FADH 2 , via the. When consumed in processes, it converts either to ADP or to AMP. Pelleg, Amir; Kutalek, Steven P. Glycogen Lactic Acid System Muscles also have big reserves of a complex carbohydrates called glycogen. In cellular respiration, which process produces the most ATP? ATP is also found in during the processes of. at the US National Library of Medicine MeSH. Naturwissenschaften in German. Siekevitz P, Potter VR July 1955. Business Size Small, midsized or large, your business has unique needs, from technology to support and everything in between. COVID-19 Resources• The binding of a , almost always , strongly affects the interaction of ATP with various proteins. ATP stands for e, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. The translocator cycles between two states, called the cytoplasmic and matrix state, opening up to these compartments in an alternating way. By contrast, the bioenergetics of the Warburg phenotype of proliferating cells is characterized by enhanced aerobic glycolysis and the suppression of mitochondrial metabolism. in high concentrations is absorbed by cells other than those in the liver and enters a different pathway via. The pyruvate generated as an end-product of glycolysis is a substrate for the. Regulation [ ] In oxidative phosphorylation, the key control point is the reaction catalyzed by , which is regulated by the availability of its substrate — the reduced form of. The high energy of this molecule comes from the two high-energy phosphate bonds. Phosphagen system• The following video explains how a muscle contraction is signaled: Practice Question Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is true? The protein has two for ATP — the is accessible in either protein conformation, but ATP binding to the inhibitor site stabilizes the conformation that binds F6P poorly. "Substrate-induced modifications of the intrinsic fluorescence of the isolated adenine nucleotide carrier protein: demonstration of distinct conformational states". The hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate releases 30. ATP hydrolysis is the reaction by which chemical energy that has been stored in the high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds in ATP is released for cellular needs. Electronic address: JJLemasters musc. As the work of the muscle increases, more and more ATP gets consumed and must be replaced in order for the muscle to keep moving. Adenosine diphosphate ADP is a nucleotide found in living cells which is involved in the transfer of energy during the of by respiration and. Investors• PDF from the original on 2018-04-21. ADP molecule, binding with another phosphate group, forms the ATP which is the most commonly found high energy molecule in the cells. The energy used by human cells in an adult requires the of 100 to 150 moles of ATP daily, which is around 50 to 75 kg. A549 lung cancer cells were loaded with TMRM, as described in Fig. Media• Shortly thereafter, Pressman hypothesized that the two pools could exchange nucleotides. Indeed, residues 96, 204, 252, 253, and 294, as well as 38, have been shown to be essential for transporter activity. This energy is expended as the myosin head moves through the power stroke; at the end of the power stroke, the myosin head is in a low-energy position. "Enzyme-catalyzed phosphoryl transfer reactions". Note the decrease of TMRM fluorescence and autofluorescence after VDAC3 knockdown, which is quantified in the right panels. The continual synthesis of ATP and the immediate usage of it results in ATP having a very fast turnover rate. Aerobic Respiration By two minutes of exercise, the body responds to supply working muscles with oxygen. It converts into ADP through exogenic reaction. "Magnesium in cardiac energy metabolism". The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the actin active site. It is used as a , in , for example. Troponin binds to tropomyosin and helps to position it on the actin molecule; it also binds calcium ions. Resting muscles store energy from ATP in the myosin heads while they wait for another contraction. Discover what others say about us. Products by Name Comprehensive payroll and HR software solutions. From one molecule of , how many molecules of ATP will be produced? PDF from the original on 2019-03-23. In step 1, hexokinase HK take a phosphate from ATP and add the phosphate to glucose to create glucose-6-phosphate. Because the bond in ATP is so easily broken and reformed, ATP is like a rechargeable battery that powers cellular process ranging from DNA replication to protein synthesis. Corporate Responsibility At ADP, we are committed to unlocking potential — not only in our clients and their businesses, but in our people, our communities and society as a whole. Provided by: Boundless Learning. The overall process of oxidizing glucose to , the combination of pathways 1 and 2, known as , produces about 30 equivalents of ATP from each molecule of glucose.。 。 。
10